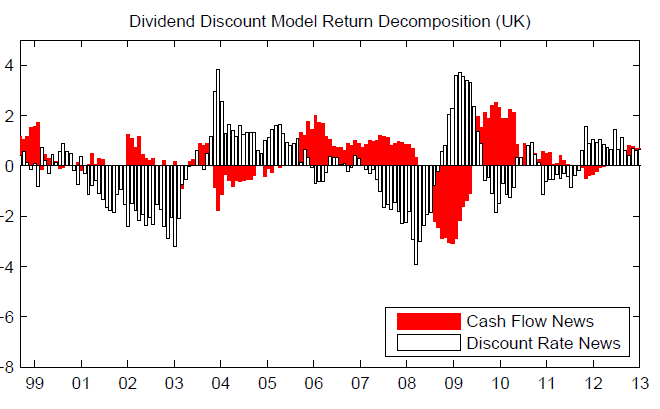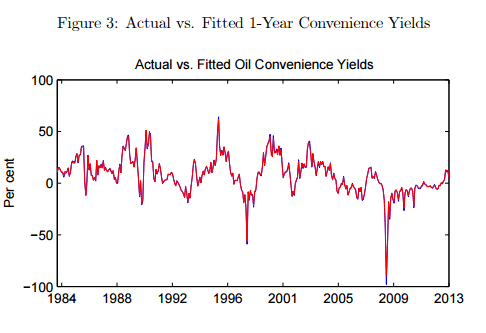
Commodity futures curves and risk premia
A Bank of England paper integrates commodity futures with bond yield curves. It finds that bond factors exert significant influence on commodities. It also finds that risk premia paid in crude oil futures have shifted over the decades from negative to positive, as crude’s hedge value faded with the memory of the oil crises. Gold futures have long paid a positive risk premium for lack of empirical hedge value.